Overview
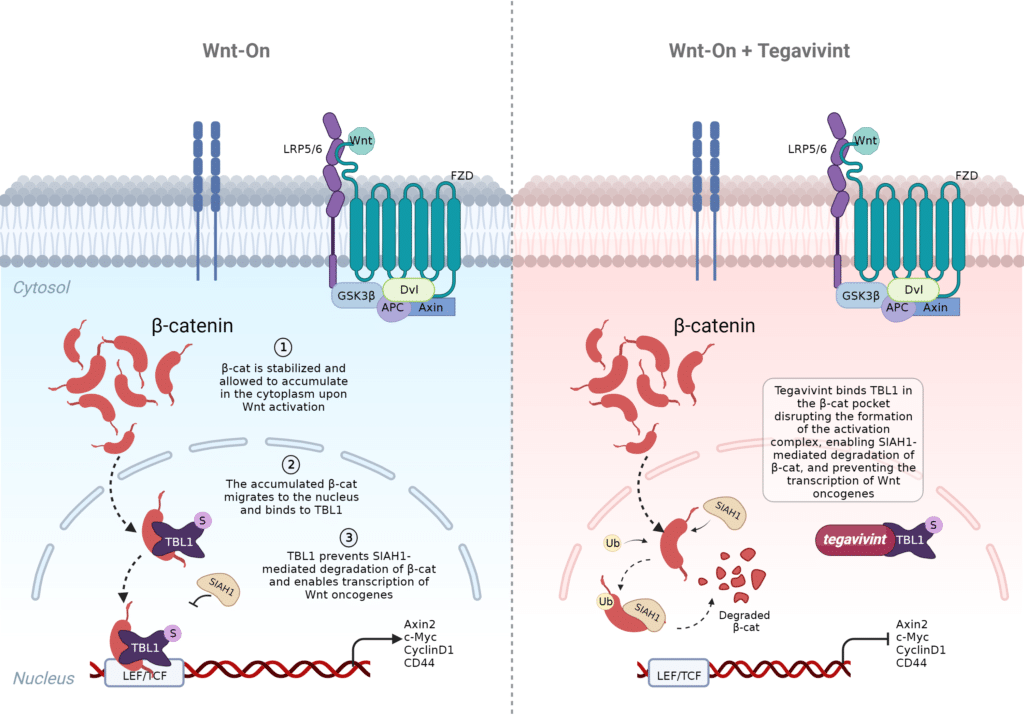
Dysregulated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is involved within several hallmarks of cancer, making it an attractive therapeutic target in oncology. Unfortunately, key members of this pathway (including beta-catenin) have either been resistant to conventional drug development or plagued with off-target toxicities. Transducin Beta-like Protein 1 (TBL1) is a newly characterized target in the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway that provides a novel way to inhibit beta-catenin oncogenic activity. TBL1 binds to accumulated nuclear beta-catenin forming an active transcription complex that prevents nuclear degradation of beta-catenin and activates genes necessary for the Wnt/beta-catenin oncogenic activity. Tegavivint is a novel, small-molecule inhibitor that binds to TBL1 and disrupts the interaction between beta-catenin and TBL1, thus promoting the degradation of nuclear beta-catenin and preventing the transcription of Wnt/beta-catenin targeted oncogenes. 1-4 Preclinical studies have shown tegavivint inhibits beta catenin activity without overt toxicity, and has been shown to not be affected by CTNNB1 gain-of-function mutations typically found in cancer cells.2-3, 5-10 In parallel with the tegavivint program, Iterion has ongoing R&D programs investigating and developing 2nd generation TBL1 inhibitors.
Our Publications
Tegavivint (BC2059) has been extensively studied in several in vitro and in vivo models with therapeutic potential in a broad range of tumors. Peer-reviewed published research articles summarizing tegavivint’s binding affinity, potency, selectivity, pharmacodynamics, and anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo can be found below.
Combination of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Panobinostat (LBH589) with β-Catenin Inhibitor Tegavivint (BC2059) Exerts Significant Anti-Myeloma Activity Both In Vitro and In Vivo
Ioanna Savvidou, Tiffany Khong, Sophie Whish, Irena Carmichael, Tara Sepehrizadeh, Sridurga Mithraprabhu, Stephen K Horrigan,…
The Small Molecule BC-2059 Inhibits Wingless/Integrated (Wnt) – Dependent Gene Transcription in Cancer through Disruption of the Transducin B-Like 1-B-Catenin Protein Complex
Raffaella Soldi, Tithi Ghosh Halder, Samuel Sampson, Hariprasad Vankayalapati, Alexis Weston, Trason Thode, Kapil N…
NUCLEAR β-CATENIN INHIBITOR – TBL1 – A Novel Target for Safe & Effective Blockade of the Nuclear β-catenin Signaling Pathway& Effective Blockade Of The Nuclear Β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Ruolan Han, PhD
Mechanistic Basis and Efficacy of Targeting β-Catenin-TCF7L2-JMJD6-MYC Axis to Overcome Resistance to BET Inhibitors
Dyana T.Saenz, PhD, Christopher Peter Mill, PhD BA, Warren Fiskus, BSc, PhD, Bernardo H Lara,…
Tegavivint and the β-Catenin/ALDH Axis in Chemotherapy-Resistant and Metastatic Osteosarcoma
Motonari Nomura, Nino Rainusso, Yi-Chien Lee, Brian Dawson, Cristian Coarfa, Ruolan Han, Jeffrey L Larson,…
Targeting nuclear β-catenin as therapy for post-myeloproliferative neoplasm secondary AML.
Saenz DT, Fiskus W, Manshouri T, Mill CP, Qian Y, Raina K, Rajapakshe K, Coarfa…
β-catenin Inhibitor BC2059 Is Efficacious as Monotherapy or in Combination with Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib in Multiple Myeloma.
Savvidou I, Khong T, Cuddihy A, McLean C, Horrigan S, Spencer A.
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of a Series of Anthracene-9,10-dione Dioxime β-catenin Pathway Inhibitors.
Soldi R, Horrigan SK, Cholody MW, Padia J, Sorna V, Bearss J, Gilcrease G, Bhalla…
Pre-clinical efficacy of combined therapy with novel β-catenin antagonist BC2059 and histone deacetylase inhibitor against AML cells.
Fiskus W, Sharma S, Saha S, Shah B, Devaraj SG, Sun B, Horrigan S, Leveque…
References:
- Soldi R. et al. J Med. Chem 2015 PMID: 26182238
- Savvidou I et al. Mol Cancer Ther 2017 PMID: 28500235
- Nomura M et al. JNCI 2019 PMID: 30793158
- Saenz DT et al. Leukemia 2019 PMID: 30575820
- Lee D.J Clin Oncol 2022 doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.11523
- Fiskus W et al. Leukemia 2014 PMID: 25482131
- Nomura M et al. JNCI 2019 PMID: 30793158
- Li J et al. Nature 2008 PMID: 18193033
- Dimitrova YN et al. J Biol Chem 2010 PMID: 20181957
- Penny MK et al. Cancers (Basel) 2023 PMID: 37509222
